Causes and Risk Factors
The most frequent causes of orbital fractures include sports injuries from balls or elbows, traffic accidents, falls, and physical assaults. Occupational accidents can also be a significant factor, especially in environments where heavy tools or machinery are used.
Protective gear, such as helmets and seatbelts, can help reduce these risks but cannot always prevent injury.
Diagnosis
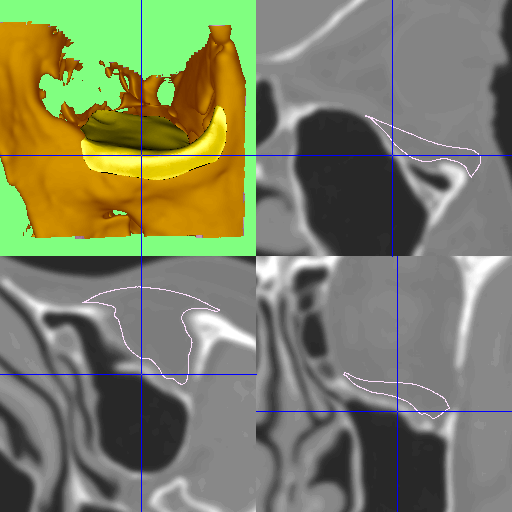
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the type and extent of the fracture. A specialist will begin with a physical examination of the eye and its movements, followed by vision testing. Imaging plays a central role, with CT scans providing the most precise information about both bone and soft tissue damage. Specialist consultation with an ophthalmologist or oculoplastic surgeon is often arranged to ensure that the health and function of the eye are thoroughly evaluated.